File formats
Files store information in particular formats, according to their function and often also the application (or applications) with which they are associated. So, you can open an image file with an application like Preview on macOS, or Adobe Photoshop.
Word-processor files
A file format is typically designated by the file’s extension, which takes the following format: .xxx. In other words, the extension contains metadata, or information about the file, typically its file type and the data it contains. A Word file is a text document produced using a word-processor and has the extension .docx.
This is also an Open XML format, which means a Word file can more easily be transferred between computers and also transformed into other document formats. It also makes it compact and modular in its structure. Because information about the file is stored together with its contents, it will open with the same appearance in a different user’s computer.
A LibreOffice file with the extension .odf is also a word-processing file. LibreOffice makes use of the OpenDocument Format. This format supports structured documents that are interoperable. This means that ODF files can be read on machines using different operating systems and with a range of different applications other than LibreOffice.
Both Word and LibreOffice store all of the information associated with a given document in the form of a compressed archive file (usually a .zip file).
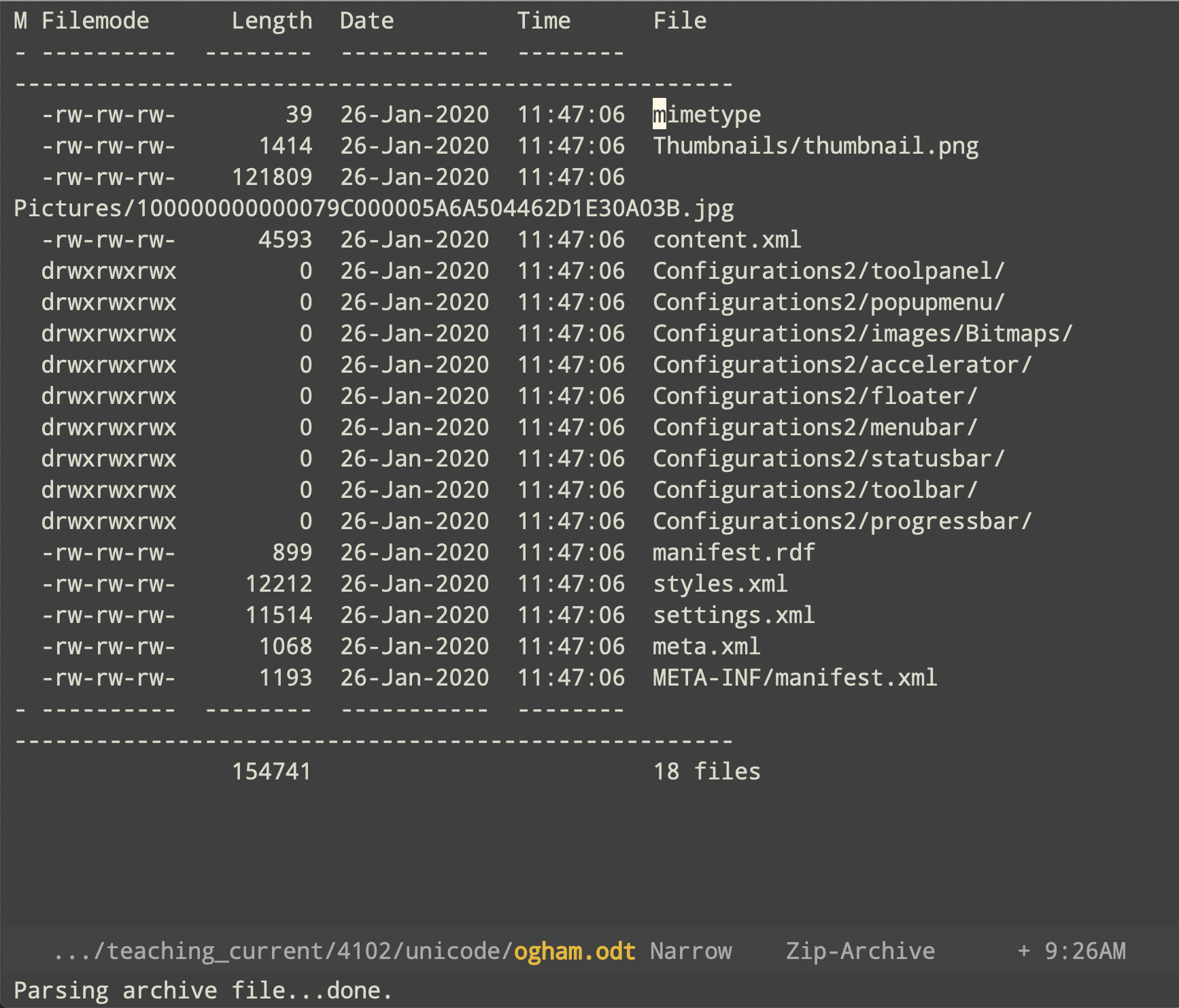
Contents of a LibreOffice template file archive in .odt format
As well as the contents of the file, this format contains information about the styles used in a given document as well as its metadata. All of this data is in the form of .xml files, a format designed for the exchange of information between computer applications. The eighteen files of which this example is made up also include an image file in .jpg format embedded in the document — it is the largest file by some margin. Finally, because these files also contain information about the configuration of the LibreOffice application in which the document was created, it too will be retrieved with exactly the same layout when opened in a different machine.
Word and LibreOffice files can also be used with Google Docs.
Plain text formats
Several file formats exist in which textual information can be encoded more simply than in a word-processing files. These are referred to as “plain text” formats because they contain only text. The simplest of these formats is a .txt file, whose contents include none of the formatting found in word-processor files.
Tip
You can see how a plain text file is different if you use theSave as command in Word to generate a file in .txt format from a word-processed document.
In Windows, you can open a .txt file using the Notepad application and in macOS with TextEdit. Both of these are plain text editors. You can also download and install other such editors, like Atom or Visual Studio Code.
Plain text files are used in the creation of corpora and you can download copies of works of literature in this format from Project Gutenberg to create a corpus of your own, or with web applications like Voyant Tools.
Binary document formats
From these examples we can conclude that the contents of a document can exist within files of different formats and that it is possible to transfer the content between formats, so that the document can then be edited using different applications. Google Docs can be used to import and can export files in a range of formats.
It is also possible to generate a file in a binary format from a word-processing document. The most common outcome of such an operation is a Portable Document Format file with the extension .pdf. Files in Word or a LibreOffice or Google Docs can be used to create a PDF.
A binary file is in a file format that contains digital data not in the form of plain printable characters. While it is now possible to transform a PDF file into a format in which it can be edited in Word, for instance, a word-processing application cannot be used to open the digital PDF file directly. Instead, you must use a dedicated application that will retain the exact appearance of the document contained in the file, like Adobe Acrobat Reader.
Because such applications exist for all operating systems and for mobile devices as well as computers, a PDF file is said to be “platform-independent”.
There are also dedicated open-source applications like AntFileConverter, which allow you to convert word-processor files or PDFs into plain text for use with corpus tools.
Image files
Most image files are also binary files containing digital data. Typical formats include .jpg, .png and .tiff files. In both .jpg and .png files, some of the binary data is compressed. On the other hand, both .png and .tiff files are “lossless”, which means that the original data can be fully reconstructed from a compressed file.
Font files
A digital typeface is typically made up of a series of font files that contain the information required to render different individual fonts, e.g. that typeface’s roman, italic and bold styles or weights. An OpenType font file contains the information needed to allow the font to be displayed using computers with different operating systems, e.g. Windows or macOS. OpenType fonts can also contain extended Unicode character sets and a range of typographic features, e.g. small capitals, non-lining numerals.
TrueType is a further scalable font format that can be accessed both in Windows and macOS. Web Open Font Format makes use of compressed font files for display in web applications.
Common file extensions and formats
- .css
- a file in Cascading Style Sheet language that controls the appearance of an HTML file on screen, in print and in other media
- .docx
- a Word text document
- .epub
- an e-book file for use with most e-book readers (note, however, that a Kindle uses files in
.azwor.azw3format); as well as text, it can support color images, graphics, interactive elements, and video files - .html
- a document in Hypertext Markup Language designed for display on the web
- .jpg
- a compressed lossy image format
- .key
- a macOS presentation file
- .md
- a Markdown document; a plain text format
- .mov
- a QuickTime video file
- .mp3
- a lossy audio format
- .mp4
- a video file format
- .odf
- a LibreOffice text document
- .otf
- an OpenType font file
- .pages
- a macOS text document
- a printable document in Portable Document Format that presents contents, images and other elements consistently from device to device
- .png
- a lightweight lossless image format
- .pptx
- a Microsoft Powerpoint file; also an Open XML Format
- .rtf
- a document data format used for saving and sharing text files
- .tiff
- a lossless image format
- .ttf
- a TrueType font file
- .txt
- a plain text document
- .wav
- a lossless audio format
- .woff, .woff2
- Web Open Font Format font files
- .xml
- a file in Extensible Markup Language used for storing and transporting information
- .zip
- an archive file format that supports lossless compression of files or directories