Digital literacy
Digital literacy consists in how you understand and engage with the processes of living, learning and working in a connected society. In many aspects of our lives, we use digital tools, sometimes pervasively. Understanding these tools extends to knowing how they operate, how best to interact with them and how to use them productively in your life and work.
In the context of your studies, you will also develop both your general and your dedicated digital knowledge and capacity. In other words, you will acquire generic skills, relevant to information technology in general. You will also acquire more specific skills and knowledge — how to use applications relevant to languages and to text in particular, and how to use this knowledge in exploring language.
In reading these pages, you will be able to explore the latter in particular, by thinking about the kinds of technologies that are relevant to your work in learning about language and languages.
A whole spectrum of skills is involved: conceptual (e.g. understanding the relationship between a language and a script), practical (e.g. how to make the most productive use of a computer keyboard), technological (e.g. how to encode transcriptions using the International Phonetic Alphabet), and cognitive (e.g. understanding how technological literacy can improve your contribute to your data and information literacy).
Learning technologies
If we adopt the perspective of the conversational framework of education, we can see how different digital technologies and tools can be mobilized, both within and beyond the classroom.
| Learning process | Digital tools and activities |
|---|---|
| Acquisition | Virtual learning environment (e.g. Canvas), online lectures |
| Inquiry | Library and internet searches, research databases |
| Discussion | Online classes (e.g. MS Teams), quizzes, discussion boards |
| Practice | Oral and written practice (e.g. word-processing, creating video clips) |
| Collaboration | Joint projects (e.g. Google Drive), online forums |
| Production | Writing essays (e.g. Office 365, Google Docs, Libre Office) |
Digital capabilities
The relevant digital skills have also been conceptualized as falling into six distinct kinds of capability, with a general understanding of information and communication technologies helping to connect them.
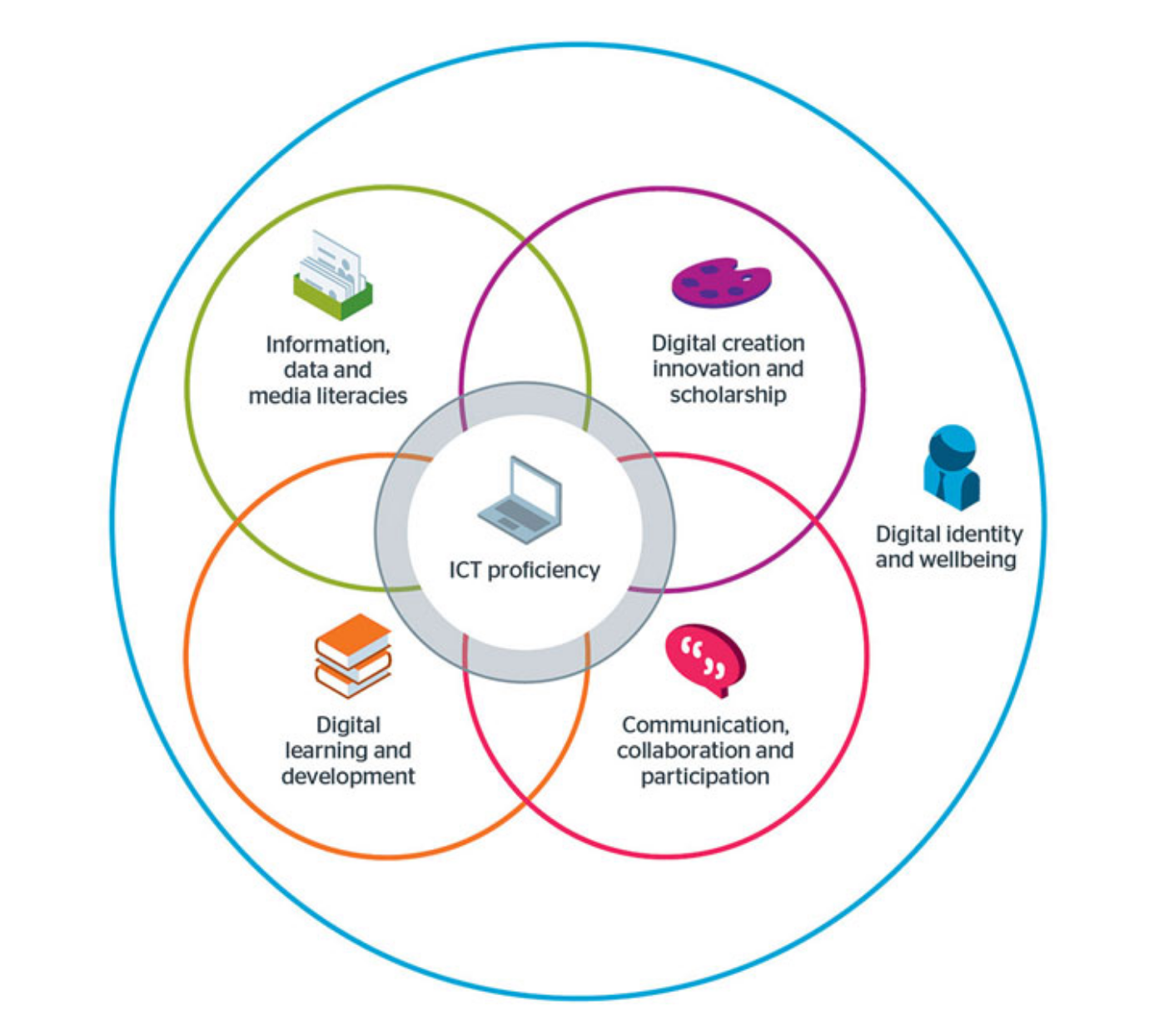
Six digital capabilities (source: JISC)
These capabilities have been extensively documented, including their critical dimension and also their important implications for your digital well-being. When thinking about how you want to develop your digital literacy, consider also these tips. The effective use of digital technologies and tools is more and more a key path to becoming a proficient independent learner.
Reflect on your experience
It is a good idea to monitor and reflect on your experience of learning technologies: in the course of your studies, you are likely to encounter many different kinds of tool and application and it makes sense to think about how these help you in your work. Expect change: new resources and ways of accessing and using information are constantly being developed, and your own work is likely to evolve in parallel. Monitor and learn from your own use of these resources and think critically about their strengths and weaknesses.